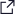Vietnam’s domestic car company VinFast is stepping up its global expansion by focusing on Asia’s emerging battery electric vehicle (BEV) markets, challenging the long-standing dominance of Japanese automakers in the region, as well as a growing number of Chinese brands.
VinFast was established by Vietnam’s largest private conglomerate Vingroup in 2017, initially to produce internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles with the technical collaboration of BMW, Magna Steyr and Pininfarina, before it began switching to BEVs in 2021 as the company refocused on future segments of the global vehicle market. The automaker launched its first BEV model in 2022, the VF e34, which has since been joined by several other battery-powered passenger models under the VF badge. The company has now ceased production of ICE vehicles altogether.
VinFast Auto was listed on New York’s Nasdaq Stock Exchange in August 2023 and its share price immediately shot up to US$82, valuing the company at a staggering US$220bn, before going into free-fall in the following months. Its share price currently trades at around US2.50, valuing the company at a more down-to-earth US$6bn.
Despite entering a growing list of overseas markets since the end of 2022, including in Europe and the US, the company struggled to grow its sales significantly last year. Global deliveries fell just short of 35,000 vehicles in 2023, most of which took place in its home market Vietnam. While this was up from the estimated 26,000 units in 2022, it was still lower than the 38,000 vehicles it delivered in 2021. Sales of electric scooters expanded threefold to just over 72,000 units, however.
VinFasts’s main production base is on Cat Hai Island in Vietnam’s northern province of Hai Phong, which the company claims has a current production capacity of some 300,000 passenger vehicles and 500,000 electric scooters per year, as well as facilities for the production of battery-powered buses.
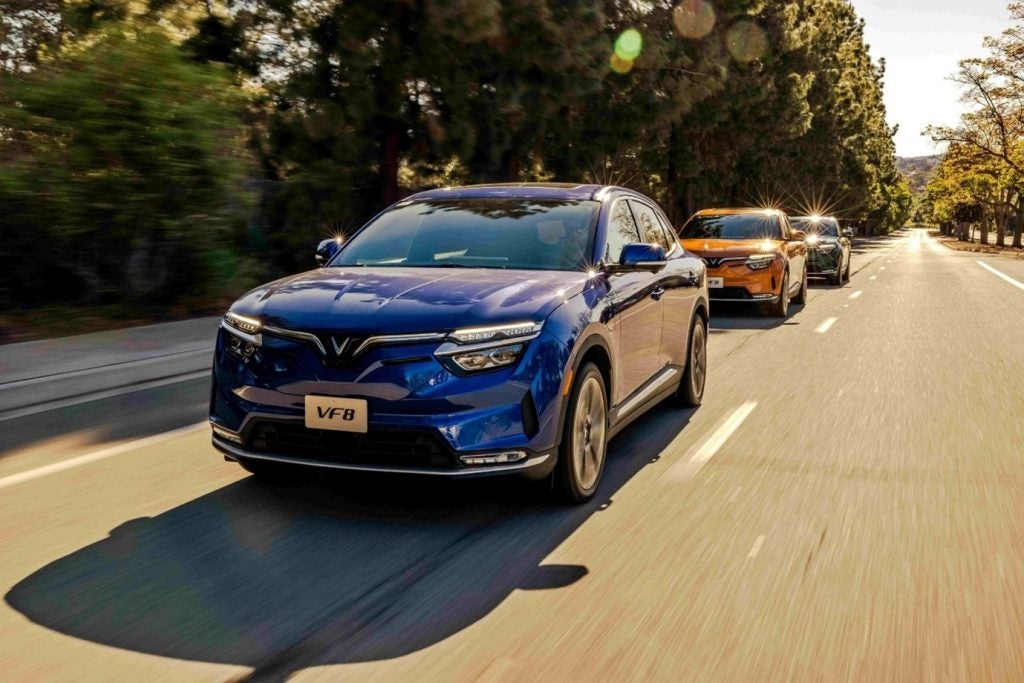
VinFast made a big splash at the recent Bangkok International Motor Show, where it displayed its current BEV range including the VF5, VF6, VF7 and VF8. It also displayed its “Wild” battery-powered pickup truck concept developed in collaboration with Australian design studio GoMotiv and first unveiled at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in the US earlier this year.
At the Bangkok show VinFast confirmed it had already recruited some 15 local dealers with plans to open 22 sales outlets across the country in the coming months. Vu Dang Yen Hang, chief executive of Vinfast Auto (Thailand), confirmed that the company would first rely on imports from Vietnam before deciding whether to produce its vehicles locally.
At the Indonesia International Motor Show (IIMS) in February VinFast also introduced its full range of right-hand drive battery-powered models, with the company confirming it will supply this market initially from Vietnam ahead of local production. Dealer recruitment began late last year and sales operations are scheduled to begin in June.
The company had previously announced plans to invest US$1.2bn to build a plant in Bekasi, a city just east of the Indonesian capital Jakarta, to produce battery-powered passenger vehicles and motorcycles and indicated it had already identified a 200-hectare plot for the facility.
Despite entering a growing list of overseas markets since the end of 2022, including in Europe and the US, the company struggled to grow its sales significantly last year.
PT VinFast Indonesia marketing director Surachman Nugroho told local reporters the plant “will supply right-hand drive electric vehicles to countries such as Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia and Australia”, adding that it will also assemble battery-powered two-wheelers. Initial production capacity will be 50,000 vehicles per year.
At the beginning of 2024 VinFast also revealed plans to invest US$2bn to build a BEV plant in India, in the southern state of Tamil Nadu, as it looks to play a major role in the country’s transition to zero-emission vehicles. The company said it will invest US$500m in an initial five-year phase of the project, with construction scheduled to start later this year.
Last year the automaker began construction of a BEV plant in the US state of North Carolina to supply the North American market from 2025. The facility will have an initial capacity of 150,000 unit/year – rising to 300,000 units if required later one. The company estimated the project could ultimately cost up to US$4bn, including facilities for the production of components such as batteries.
VinFast said it increased its global revenues by 91% to almost US$1.2bn last year, while incurring a gross loss of US$552m. The company said it has US$1.8bn in cash on hand and available reserves in the form of grants and other facilities. It will likely need much more fresh cash over the next few years to carry out its ambitious business plan.
In its latest financial presentations, VinFast has said it is targeting 100,000 global BEV sales in 2024 and expects to have 400 sales outlets in place globally by the end of the year – up from 123 at the end of last year.
With Chinese automakers rapidly expanding their global operations, the global market for BEVs has becoming extremely competitive over the last year. Sales growth is slowing and government incentives are being but cut, forcing leading brands including Tesla to offer deep discounts to help drive up sales. It is not an easy marketplace for the less established companies and brands, but VinFast cannot be accused of not giving it a good go.